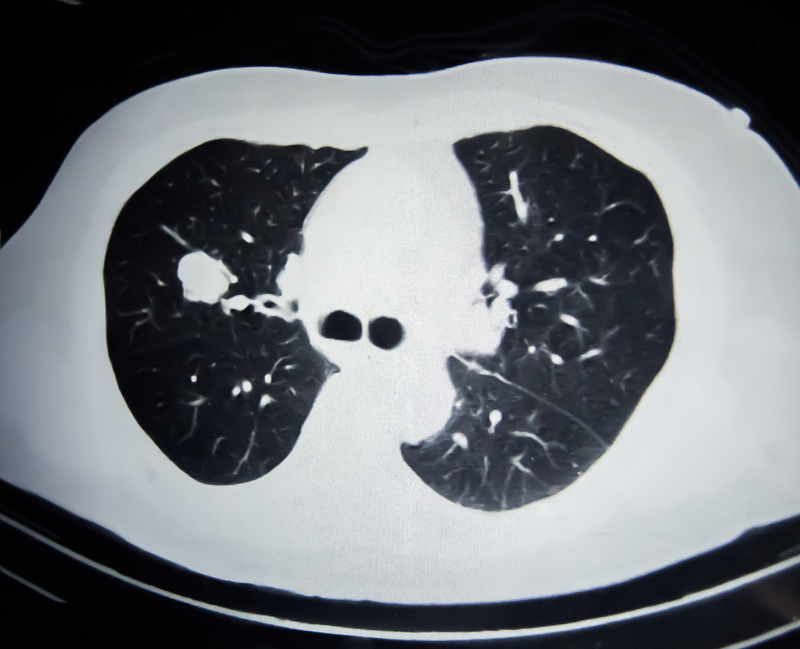
African American cancer survivors should make a deliberate effort to stop smoking because cancer recurrence or return was much higher in cancer patients who continued to smoke. In this study done at Wayne State in Detroit, Black patients were more likely to continue to smoke after being diagnosed with cancer and were more likely to continue if their partner continued to smoke.
A longer smoking history and living with a smoker increased the odds of continued smoking after a cancer diagnosis. Over all, lung cancer survivors were most likely to quit after diagnosis.
These findings are similar to other ethnic populations and highlight that continued smoking after a cancer diagnosis is both common and highly risky. Stopping smoking must remain a primary priority for patients diagnosed with cancer because, by continuing smoking, their risk of cancer returning and spreading is much higher.
Health care providers like doctors and nurse practitioners should emphasize the importance of both the patient and other house members (wife, husband, adult children, etc.) stopping smoking because their success rates are linked.

Take a listen to my podcast on menthol cigarettes and why they may be the worst type of cigarette.
And here is another Better Black Health podcast episode talking about how cigarettes may be contaminated by pesticides and may be why smoking raises your risk for diabetes.